Types of Women’s Belly & Belly Fat: Causes and Solutions
Introduction
Belly fat is a common concern among women, impacting health, confidence, and overall well-being. Understanding the types of belly fat and their causes is crucial for effective management. This article explores different belly shapes, types of belly fat, contributing factors, and ways to manage them effectively.
Types of Women’s Belly Shapes
Women’s belly shapes vary based on genetics, lifestyle, and health conditions. The most common belly types include:
1. Hormonal Belly
Characteristics:
Soft and round, accumulating around the lower abdomen.
Often linked to hormonal imbalances like PCOS, menopause, or thyroid issues.
Causes:
Excess estrogen or cortisol.
Insulin resistance.
Stress-induced weight gain.
Solutions:
Balancing hormones through diet (fiber-rich, low-sugar foods).
Engaging in stress-reducing activities like yoga and meditation.
Consulting a doctor for potential hormone therapy.
2. Stress Belly
Characteristics:
Hard belly fat, mostly around the upper stomach.
Feels firm due to cortisol-driven fat accumulation.
Causes:
Chronic stress leading to high cortisol levels.
Poor sleep patterns.
Overconsumption of caffeine and processed foods.
Solutions:
Managing stress through relaxation techniques.
Cutting back on caffeine and processed foods.
Ensuring proper sleep hygiene.
3. Mommy Belly (Post-Pregnancy Belly)
Characteristics:
Loose skin and excess fat in the lower belly.
May include a separation of abdominal muscles (diastasis recti).
Causes:
Postpartum hormonal changes.
Weakened core muscles.
Excess fat storage during pregnancy.
Solutions:
4. Bloated Belly
Characteristics:
Swollen stomach that fluctuates in size.
Often associated with gas and digestive discomfort.
Causes:
Food intolerances (gluten, dairy, etc.).
Poor digestion or gut health.
Dehydration and excessive sodium intake.
Solutions:
Eating fiber-rich foods and staying hydrated.
Identifying and eliminating trigger foods.
Probiotics and digestive enzyme supplementation.
5. Menopausal Belly
Characteristics:
Weight gain around the midsection.
Increased fat storage due to hormonal changes.
Causes:
Decreased estrogen levels slowing metabolism.
Muscle loss due to aging.
Insulin resistance and increased cravings.
Solutions:
Strength training to maintain muscle mass.
Balanced diet with lean proteins and healthy fats.
Hormone therapy if recommended by a doctor.
6. Beer Belly (Visceral Fat Belly)
Characteristics:
Hard fat accumulated deep inside the abdomen.
Causes a rounded, protruding belly.
Causes:
Excessive alcohol consumption.
Poor diet and lack of exercise.
Genetic predisposition to visceral fat storage.
Solutions:
Reducing alcohol intake.
Following a Mediterranean-style diet.
High-intensity workouts to burn visceral fat.
7. Skinny Fat Belly
Characteristics:
Small frame but a noticeable belly bulge.
Lack of muscle tone and higher fat-to-muscle ratio.
Causes:
Sedentary lifestyle.
Poor nutrition with excessive carbs and low protein.
Genetic predisposition.
Solutions:
Strength training to build muscle.
Protein-rich diet.
Active lifestyle with regular movement.
Types of Belly Fat
Belly fat is categorized into two main types:
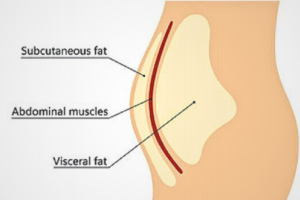
1. Subcutaneous Fat
Located under the skin and is soft and pinchable.
Less harmful but contributes to obesity.
Can be reduced through exercise and diet.
2. Visceral Fat
Stored around internal organs.
More dangerous as it increases the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Requires targeted lifestyle changes for reduction.
Factors Contributing to Belly Fat
1. Poor Diet
High consumption of processed foods, sugars, and trans fats.
Lack of fiber and protein in meals.
2. Lack of Physical Activity
Sedentary lifestyle leads to fat accumulation.
Insufficient cardio and strength training.
3. Hormonal Imbalances
Cortisol, estrogen, and insulin imbalances contribute to belly fat.
4. Poor Sleep Patterns
Sleep deprivation disrupts metabolism and increases cravings.
5. Stress and Mental Health
Chronic stress leads to higher cortisol levels, causing fat storage in the abdomen.
Effective Ways to Reduce Belly Fat
1. Diet Modifications
- Eat whole, nutrient-dense foods.
- Reduce sugar, alcohol, and processed food intake.
-
Increase fiber, protein, and healthy fat.
2. Exercise Strategies
Strength training and resistance exercises.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) for fat loss.
Core exercises for abdominal toning.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Managing stress through meditation and mindfulness.
Prioritizing sleep and maintaining a regular schedule.
Staying hydrated and practicing portion control.
Conclusion
Understanding the type of belly and the causes of fat accumulation helps in choosing the right approach to achieve a toned and healthy body. A combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications is key to reducing belly fat and improving overall well-being.

